How GIF Works? And How Can You Convert Any Image into a GIF?
GIFs (Graphics Interchange Format) have taken over the internet. From memes to tutorials, GIFs are everywhere! But have you ever wondered how GIFs work? And how can you convert an image into a GIF? I’ll break it down in this detailed guide in a simple, engaging way.
What is a GIF?
A GIF (Graphics Interchange Format) is a digital image format that supports animation. Unlike still images like JPEGs or PNGs, GIFs can display multiple frames in succession, creating the effect of movement.
GIFs were first introduced in 1987 by CompuServe and have since become a staple in digital communication. They are particularly popular in memes, social media reactions, advertisements, and tutorials. The GIF format uses lossless compression, meaning it retains its quality even after compression.
However, GIFs are limited to 256 colors, making them less vibrant compared to modern video formats. Despite this, they remain widely used due to their small file sizes, ease of sharing, and ability to autoplay without requiring a video player. Because of their looped nature, GIFs can capture attention quickly and convey emotions effectively in digital conversations. Whether you use GIFs for fun, marketing, or educational purposes, understanding how they work and their advantages can help you make the most of this universalformat.
How Does a GIF Work?
GIFs work by displaying a series of frames in rapid succession, creating the illusion of motion. This is similar to how flipbooks work—each frame is a still image, but when played in sequence at a specific speed, it creates smooth animation. A GIF consists of multiple static images (frames) that are combined into a single file.
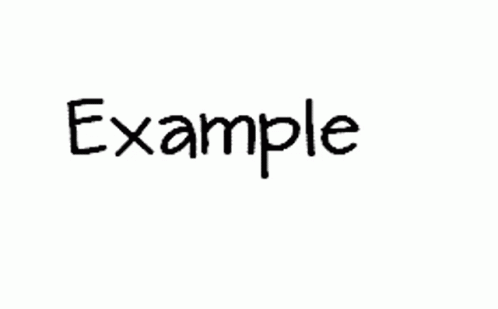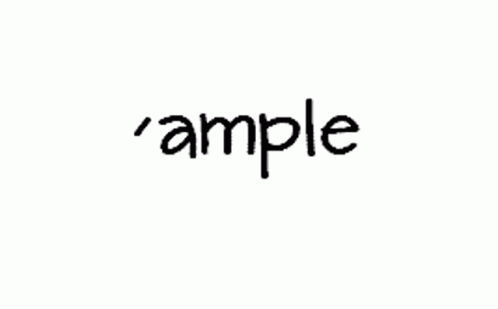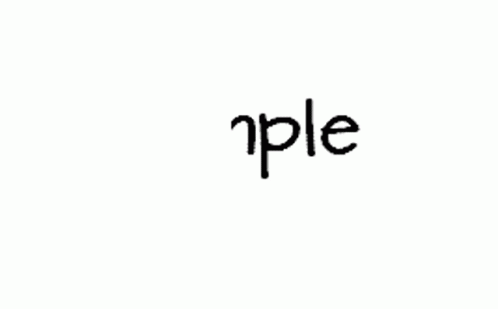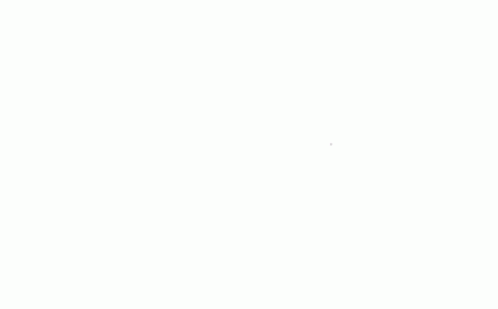
The playback speed is determined by frame delay, which is measured in milliseconds. For instance, if each frame is displayed for 100ms (0.1 seconds), the animation will appear fast, whereas a 500ms delay will make it slower.
GIFs also support looping, meaning the animation can repeat indefinitely. This is why GIFs are commonly used in memes and reaction images—they continuously loop without requiring any user input. Additionally, GIFs use Lempel-Ziv-Welch (LZW) compression, which allows them to maintain quality while keeping file sizes small. Some GIFs even include transparency, enabling them to blend seamlessly into different backgrounds. Understanding how GIFs function helps creators optimize their animations for better performance and visual appeal.
Why Are GIFs So Popular?
GIFs have gained massive popularity because they are lightweight, easy to share, and visually engaging. In a digital age where attention spans are short, GIFs deliver quick, impactful messages without requiring long videos or text explanations.
Their autoplay feature makes them perfect for capturing attention in social media feeds, online articles, and even advertisements. Platforms like Giphy and Tenor have made GIFs even more accessible, allowing users to search and share millions of pre-made animations instantly.
Another reason for their popularity is their emotional expressiveness—whether it’s a funny reaction, a celebratory moment, or an instructional clip, GIFs convey emotions better than static images. They also bridge the gap between images and videos, providing a middle-ground solution that loads quickly without taking up too much bandwidth.
Businesses use GIFs for marketing, educators use them for quick tutorials, and individuals use them in conversations to enhance engagement. The versatility and ease of use make GIFs a dominant form of digital expression in today’s online culture.
How to Convert an Image into a GIF?
Converting an image into a GIF is easier than ever, thanks to various online tools, software programs, and mobile apps. The process involves taking one or more still images and adding animation effects such as transitions, movement, or looping.
If you only have a single image, you can animate it by adding effects like zoom, fade-in, or motion blur. If you have multiple images, you can create a slideshow-style GIF where each image appears for a set duration before transitioning to the next.
The key aspects to consider are frame rate, resolution, and file size—higher frame rates create smoother animations but result in larger files. Many free and paid tools are available to assist in this process. Whether you prefer an online converter, professional software like Photoshop, or a mobile app, each method has its advantages. By choosing the right tool, you can easily transform static images into eye-catching, shareable GIFs tailored for social media, websites, or personal projects.
Method 1: Using Online Tools (No Software Needed)
Online GIF converters are the easiest way to create a GIF without installing any software. Websites like EZGIF, Giphy, and Canva provide user-friendly interfaces where you can upload an image, adjust settings, and generate a GIF in minutes.
The biggest advantage of online tools is their accessibility—since they run in a browser, they work on any device with an internet connection. To create a GIF using an online tool, simply upload your image(s), set the frame delay, choose loop settings, and apply effects if needed.
Once satisfied, you can download and share your GIF instantly. Some tools even allow additional customizations like adding text, stickers, and filters. However, online tools often have file size limits and may reduce quality due to compression. If you need a quick, hassle-free solution, online GIF makers are a great option for beginners and casual users who want to convert images into GIFs without complex editing software.
Method 2: Using Photoshop (For Professionals)
Adobe Photoshop is one of the most powerful tools for creating and editing GIFs, making it a preferred choice for professionals. Unlike online tools, Photoshop offers precise control over animation, allowing users to fine-tune every aspect of their GIF.
To create a GIF in Photoshop, start by importing your image(s) into different layers. Then, open the Timeline panel and create an animation by setting each layer as a frame. Adjust the frame duration, loop settings, and transition effects to achieve the desired animation style. Photoshop also enables users to apply filters, effects, and advanced blending options for a polished look.
Once done, export the GIF using the Save for Web (Legacy) option to optimize file size and quality. While Photoshop offers advanced customization, it requires a learning curve and a paid subscription. However, for professionals and designers who need high-quality, customized GIFs, Photoshop remains an unbeatable tool with unmatched flexibility.
Method 3: Using Mobile Apps (For Beginners)
For those who prefer working on smartphones, mobile apps provide a simple way to create GIFs on the go. Apps like GIF Maker, ImgPlay, and GIF Me! Camera are designed to help users convert images into GIFs quickly.
The process is straightforward—upload an image, choose animation settings, and export your GIF. Most apps also include stickers, text overlays, filters, and transition effects, allowing for creative customization. One of the biggest benefits of mobile apps is convenience—you can create a GIF anytime, anywhere, without needing a computer.
However, mobile apps may have limitations in terms of file size, resolution, and editing features compared to desktop software. Still, for beginners and casual users who want to make fun, shareable GIFs without technical expertise, mobile apps are a great option. Whether you’re creating GIFs for social media, messaging apps, or personal use, mobile apps make the process effortless and enjoyable.
Got Questions?
If you have any doubts drop a comment below, Thanks for reading our blog!